France is one of the countries most affected by climate change
France is facing a significant challenge as one of the countries most affected by climate change. With cyclonic episodes, floods, extreme heatwaves, and droughts becoming increasingly common, the impact on the country is profound. A recent EU Copernicus report underscores the alarming rise in temperatures and the subsequent effects on Europe. This article delves into the key findings of the report and explores how France is grappling with these climate challenges.
The Growing Threat of Climate Change
France is at the forefront of the climate crisis, experiencing a variety of extreme weather events that are becoming more frequent and severe. The nation’s geographical diversity, ranging from coastal regions to mountainous areas, makes it particularly vulnerable to the multifaceted impacts of climate change. The EU Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) provides vital data and insights into the changing climate patterns across Europe. The latest report reveals startling trends, emphasizing the urgent need for action to mitigate and adapt to these changes. France, as one of the most affected countries, serves as a case study for understanding the broader European climate crisis.
2023: The Hottest Year on Record in Europe
The year 2023 set a new record as the hottest year in Europe’s history. This unprecedented heatwave had far-reaching effects on ecosystems, agriculture, and human health. The temperature spikes were particularly pronounced in Southern Europe, with France experiencing some of the highest temperatures recorded. The frequency and intensity of extreme weather events such as droughts, floods, and fires have surged. These events not only cause immediate damage but also have long-term repercussions on the environment and the economy. The report indicates a worrying trend that these events will become more common as global temperatures continue to rise.
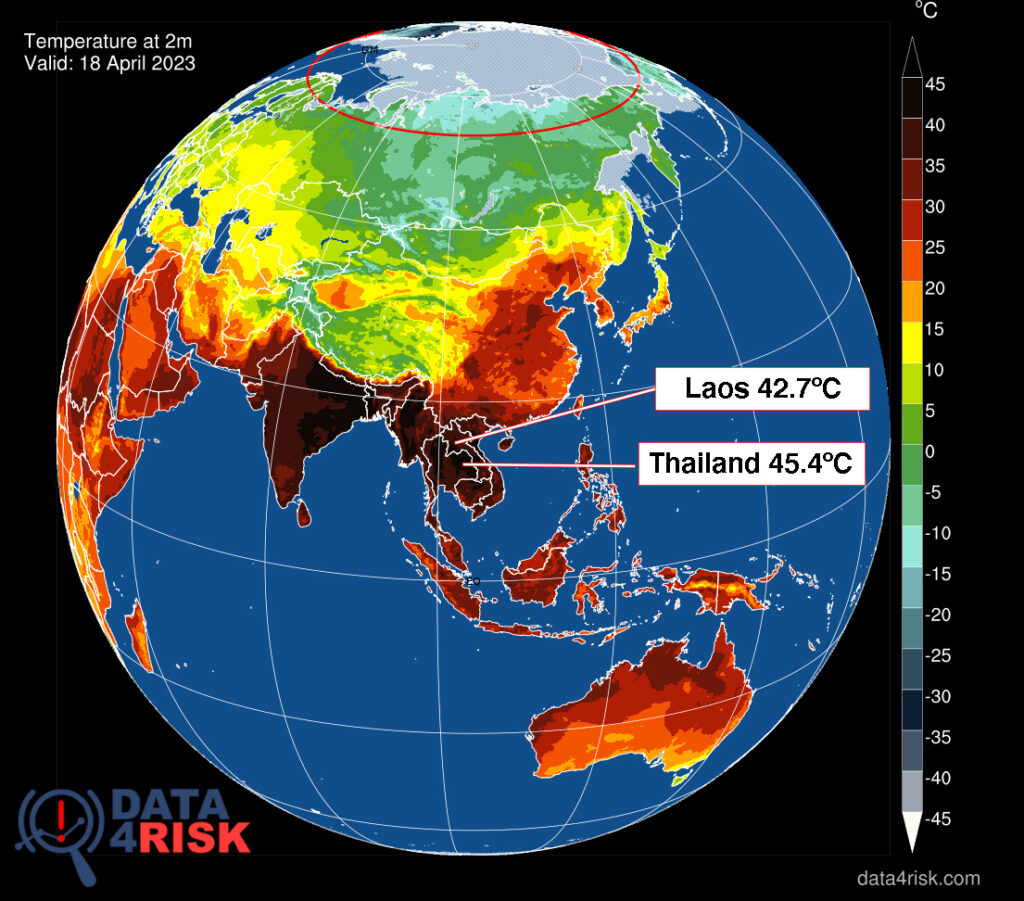
The financial cost of climate-related disasters is escalating. Heat stress, in particular, poses significant health risks, leading to increased mortality rates during heatwaves. The economic losses due to damaged infrastructure, lost agricultural productivity, and healthcare expenses are mounting, putting additional strain on national resources.
Cyclonic Episodes and Their Impact
Cyclonic episodes have become more frequent and intense, bringing destructive winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surges. These events lead to severe flooding, property damage, and loss of life. The changing climate is likely to increase the intensity of these cyclones, making them more dangerous and harder to predict.
Recent cyclones, such as Storm Alex in 2020, have caused significant devastation in parts of France. These storms highlight the need for improved forecasting and better infrastructure to withstand such extreme weather. The aftermath of these events underscores the critical importance of preparedness and resilient building practices.
Major Flood Events in France
Flooding remains one of the most persistent and damaging consequences of climate change in France. The country has experienced numerous major flood events, including the Seine flood in 2016 and the recent flash floods in the South. These events cause widespread destruction, disrupt lives, and have long-lasting economic impacts.
Efforts to mitigate flood risks include the construction of levees, improved drainage systems, and the restoration of natural floodplains. Emergency response strategies are also critical, involving early warning systems, evacuation plans, and community education to reduce the impact of floods on vulnerable populations.
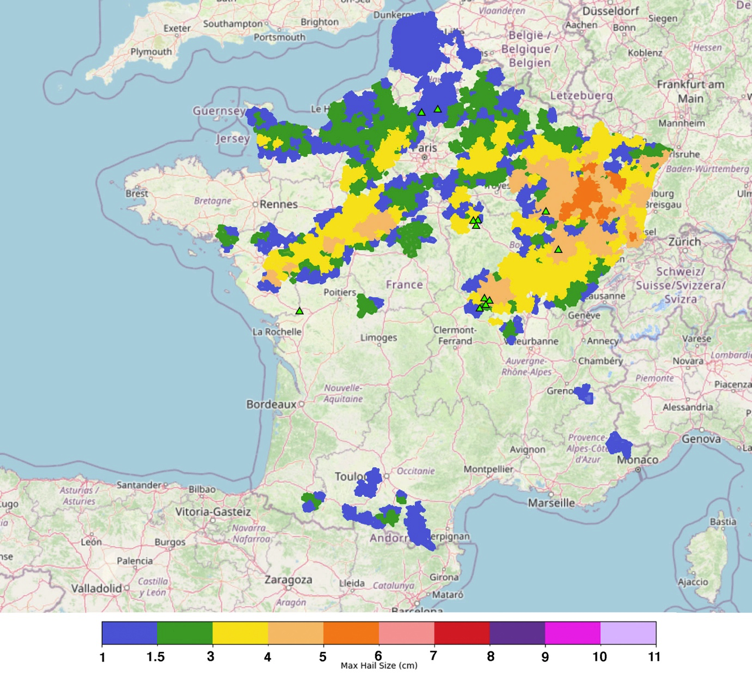
Record-Breaking Temperatures
France has seen record-breaking temperatures, particularly during the summer months. These heatwaves pose severe health risks, especially to the elderly and those with pre-existing health conditions. The agricultural sector is also heavily impacted, with crops suffering from the extreme heat and lack of water.
Droughts exacerbate the stress on water resources, affecting both agriculture and natural ecosystems. Reduced crop yields and increased irrigation demands strain the agricultural sector, while forests and wildlife habitats suffer from the lack of moisture. This ecological imbalance leads to a loss of biodiversity and increased susceptibility to wildfires.
Role of Technology in Mitigation
Technology plays a crucial role in climate mitigation efforts. Advanced weather forecasting, satellite monitoring, and AI-driven analytics help predict and respond to extreme weather events more effectively. These technological advancements are vital for planning and implementing effective climate adaptation strategies.
Data4Risk specializes in providing crucial insights into future climate conditions based on the latest RCP scenarios 2.6, 4.5, and 8.5. We empower you to make informed decisions, whether you’re planning infrastructure, managing resources, or mitigating risks related to storms, hail, flood, drought and wildfires based on the state-of-the-art numerical data. It seems that we already have crossed the line of the RCP2.6 scenarios and head to the pessimistic climate scenarios.
